What a tick bite looks like on a person’s body, photo and symptoms
Content
- 1 Description and lifestyle
- 2 Types of "bloodsuckers"
- 3 As the tick bites
- 4 What does a tick bite look like
- 5 How to determine the tick bite
- 6 What can be infected by a tick bite
- 7 What to do if bitten by a tick - instruction
- 8 First aid for tick bites
- 9 Tick bites in children
- 10 What not to do with tick bites
- 11 Bite prevention
- Mite
- Types of ticks
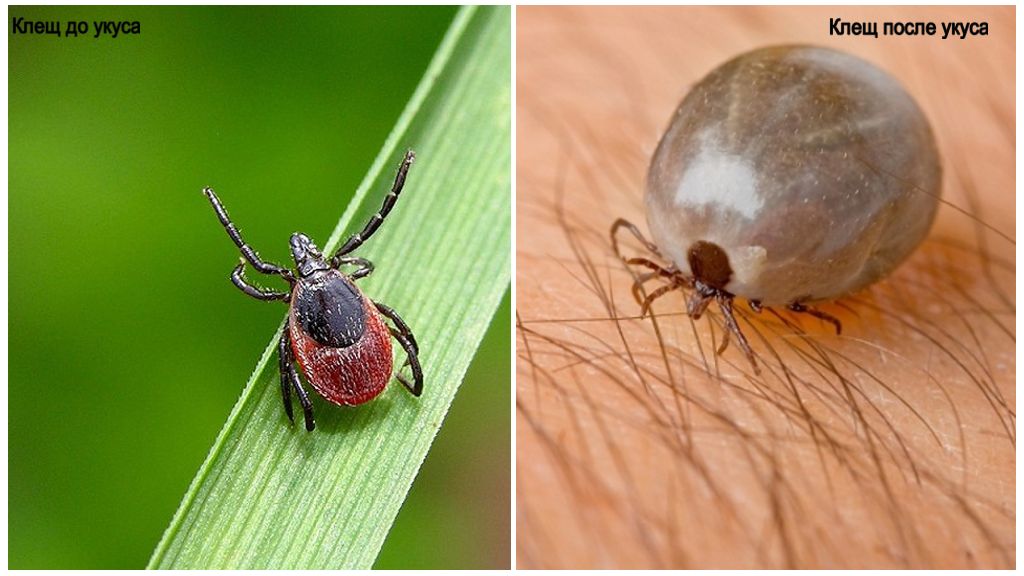
- Tick before bite and after
- Tick bite
- Negative symptoms after a tick bite
- Symptoms of disease after being bitten by an infected tick
- First aid for tick bites
- Children's tick bite
Summer brings not only sunny weather and the possibility of outdoor recreation, but also a high probability of getting a tick bite. Such a nuisance is associated not only with the problems of removing the parasite from the body and subsequent treatment, but also with the ability to tolerate some infectious diseases that are dangerous to the health of people whose symptoms you need to know to avoid further complications or infectious diseases.
Description and lifestyle
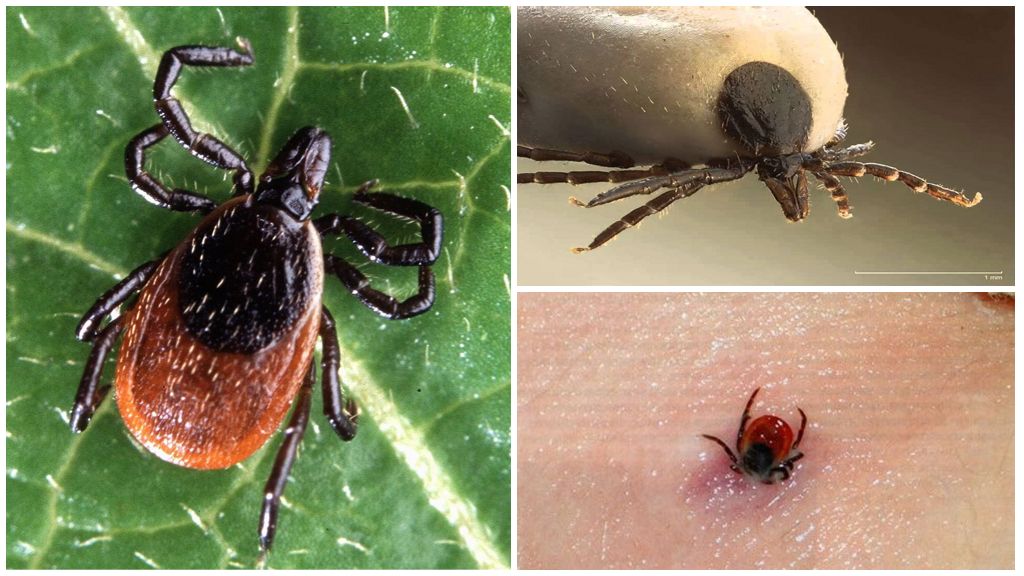
Ordinary mites, which are common in central Russia, live in the forest among the foliage and in garden plots, that is, everywhere where there are any planting of plants. They belong to the order of small arachnids (Latin Acarina), a subclass of arthropods. The size of the tick before the bite is usually 0.4-0.5 mm, occasionally it can reach 3 mm.
The parasite's torso consists of 2 parts and 6 pairs of appendages: 4 of them are legs, the pair are pedipalps, and the most front ones are chelicera-like claws that form a cutting-piercing mouth, which can be clearly seen in an enlarged photo of an ordinary tick.
On a note!
The active period of ticks begins in May-June and lasts the entire warm season, the maximum risk of bites falls on dry and warm weather.The basis of their food is human blood and mammals, which they drink with the help of a special organ, as can be seen in the photo of the tick's proboscis. They define the approach of the victim by smell at a distance of 10-15 m.
The danger of tick bites is that they instantly pierce the skin along with the proboscis and the head, then they begin to suck blood, that a person cannot always understand that a tick bit because of its small size. And only when the parasite is inflated from drunk blood, it increases and becomes noticeable on the body. Then the victim, having found a tick, can begin measures for its removal and treatment of the bitten place.
Therefore, it is better to know in advance how long a person’s tick bite symptoms appear in order to take measures and clarify the possibility of infection from any infections.
Types of "bloodsuckers"
The most common types of ticks found in Russia:
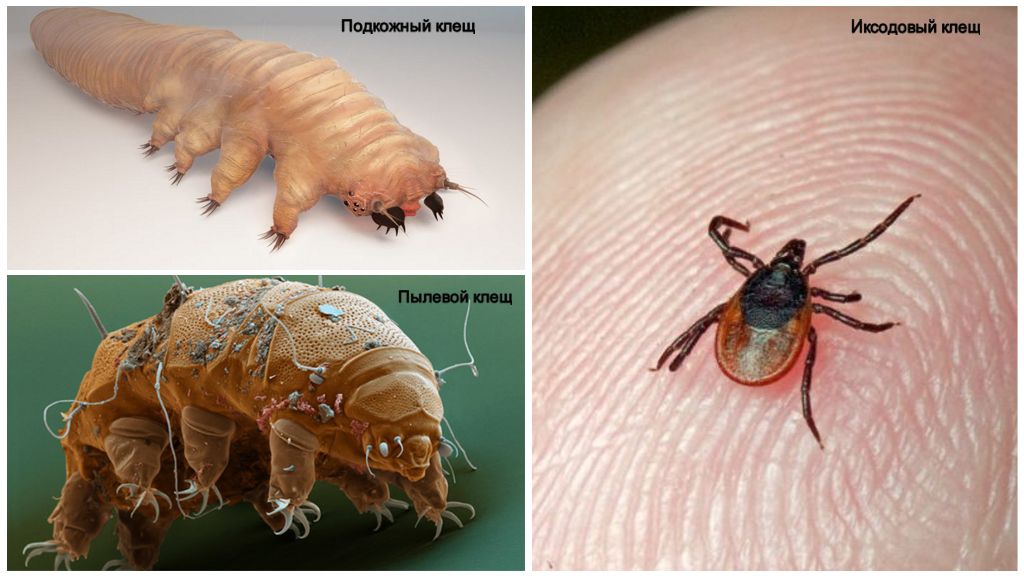
- Ixodic (lat. Ixodidae) - the most dangerous for humans, belong to the family of blood-sucking, parasitic animals. Its largest representatives in the usual state have a length of 1.3 cm, and after consuming a portion of blood - up to 2.5 cm, as can be seen in the photo of the pumped tick.After implantation under the skin, the mite is fixed there with a special growth in the mouth, therefore, when the parasite's head is pulled out, it remains in the host's body.
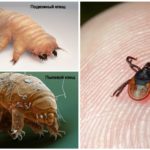
- Demodex or subcutaneous - refers to opportunistic, permanently living on the skin of a person on the face and other areas. It lives at the base of the hair follicles and feeds on skin particles and the secreted lard from the glands. Activation of parasites occurs with a decrease in immunity or hormonal imbalance and is expressed in the inflammatory process and the appearance of acne and ulcers. The smallest size of demodex (0.3 mm), allows you to see on the photo of a sucked tick under the skin only at high magnification under a microscope.
- Bed parasites or dust (size 0.1-0.2 mm) - live only in bed linen. Their diet is not blood, but dead skin particles. Leaving on the human body the results of their vital activity, such small ticks can cause a strong allergic reaction on the body of their victim. Photos of ticks are presented below.
As the tick bites
Directly during the bite, the parasite injects an anesthetic substance, so the victim does not feel the process of being bitten by a tick, and during this time the parasite has time to begin to drink blood.And only after 15-20 minutes, when a red spot appears and itches, their reason becomes clear.
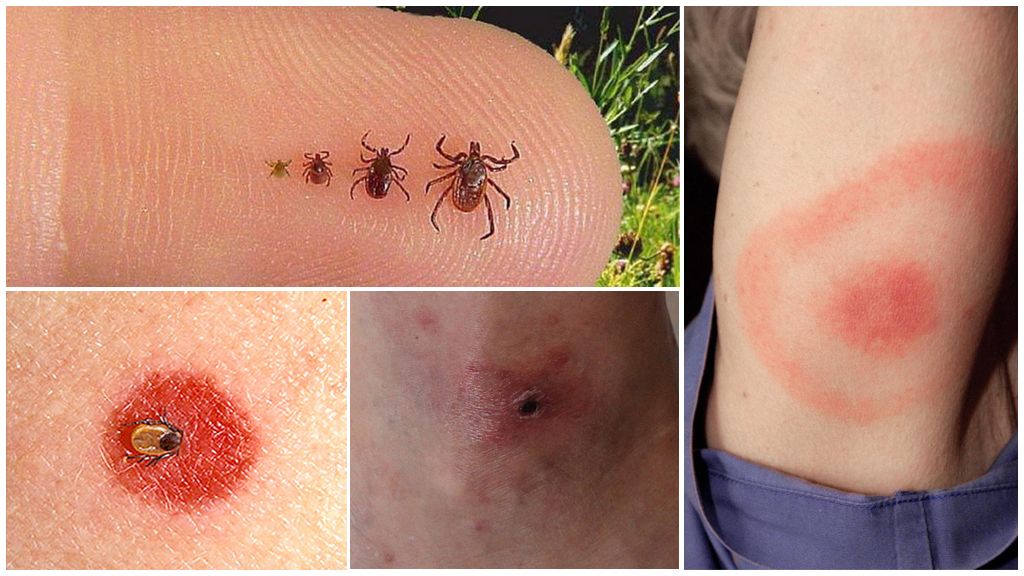
Moreover, the male tick after a bite, drunk, immediately disappears, but the female, as seen in the photo of the tick before and after the bite, with the absorption of blood greatly increased in size. She can cling so tightly to the skin, getting there with her head and proboscis, that it will be very difficult to get it.
On a note!
After sticking, a tick can stay on the body for several days, until the person notices him or he disappears by himself.
Ticks are carriers of some diseases that are dangerous to humans: infectious encephalitis, borreliosis, tularemia, etc. If the parasite is infected with a virus, it can infect its prey by injecting saliva. However, the first symptoms do not appear immediately, but only after 7-24 days after the bite, and occasionally after 1-2 months.
On a note!
The duration of the incubation period after a tick bite depends on the state of health of the victim and his blood brain barrier.
The area on the body of the victim, he chooses, based on the softness of the tissues of the skin. The most common places for tick bites on a person’s body are:
- chest, armpit, neck;
- place behind the ears;
- abdomen and groin area;
- loin;
- the inside of the elbows on the arms and the legs on the legs, below the knees;
- in the middle of hair in the head;
- limbs and exposed skin.
It is recommended to inspect these zones in order to find a tick after each walk in nature and a picnic trip.
What does a tick bite look like
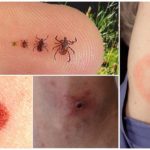
Most often, a person at first does not notice the parasite on the skin, because externally, you can confuse the tick with a small mole. It becomes noticeable when it swells from drunk blood, but has not yet managed to fall off on its own. There is redness, slight swelling or bump in the affected area, as seen in the photo of a tick bite, as well as burning or itching sensations. Some people with hypersensitivity may have allergic reactions.
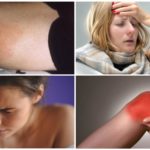
In rare cases, negative symptoms appear after a tick bite, especially when infected with a disease:
- a bite site, swelling of surrounding tissues, shortness of breath;
- rash over the whole body;
- headache, chills, fever;
- photophobia;
- joint pain, numbness of certain areas or limbs;
- difficulty walking due to paralysis of the legs;
- sleep disturbance, loss of appetite.
Important!
With an acute reaction to a tick bite, abrupt attacks of nausea and vomiting, a temperature jump, extensive edema, tachycardia, or even fainting, an ambulance must be urgently called.
How to determine the tick bite
To determine by the appearance of the affected place, which insect has bitten a person, it is possible only by some signs. This is especially difficult to do if there was a tick bite without a tick, which has already disappeared by itself.
Important!
A characteristic feature that makes it possible to distinguish a tick bite is the annular shape of the affected zone: in its middle is the center of red, surrounded by rims, initially pale, then bright. Such rings are clearly visible on the above photograph of the trail of a tick bite in a person, regardless of whether there is a parasite attached to it.
After the "bloodsucker" disappears by itself, or is removed, the victim remains a dense, but not very painful blister with a hole from the trunk.
What can be infected by a tick bite
The list of diseases that can be tolerated by “bloodsuckers” reaches 60, but the most common ones will be considered in more detail. The above symptoms will help a person whose tick bit into his head, leg, or other parts of the body to follow his state of health, in time to notice his deterioration and consult a doctor for treatment.
Tick-borne encephalitis
This is a viral disease that affects the human nervous system. The incubation period is 4-14 days. Then the infection causes the following unpleasant symptoms:
- sharp increase in body temperature;
- muscle weakness, numbness of the limbs and neck;
- redness of the face, eyes and oral mucosa;
- severe headaches;
- loss of appetite, nausea and vomiting.
Important!
The negative effects of a tick bite in this disease are quite severe: neurological pathologies, personality changes, disability and even death. The first symptoms of the disease may occur within a week after infection, it is possible to carry out prevention.
Lyme disease or borreliosis
The disease is transmitted by bacteria that cause intoxication of the body.The incubation period: 5-14 days, the disease goes through several stages, the primary symptoms are similar to a cold, and then comes a latent form that takes several months, during which damage to the joints and important organs of a person occurs.
Symptoms of infection are expressed in the following:
- sharp rise in temperature;
- pain in the head, constant fatigue;
- the tick bite is swollen and reddened, then a specific erythema of 10–20 cm in size appears, which gradually swells and transforms from a red spot into a ring with a diameter of up to 60 cm, in the center its color changes to light cyanotic;
- a few days later a crust or scar forms, which disappear after 12-14 days.
Such a disease after a tick bite causes damage to the nervous, cardiovascular and motor systems, which can lead to disability.
Hemorrhagic fever
The disease is transmitted by a virus, the main symptoms of which are: a sharp rise in temperature and an incipient fever, hemorrhages in the upper layers of the skin, a change in the composition of the victim's blood. Experts subdivide the disease into 2 types: Omsk and Crimean fever. Timely diagnosis and treatment of a tick bite (antiviral drugs, vitamins for blood vessels) help to successfully cope with such a disease.
On a note!
The carriers of these diseases are not all "bloodsuckers" who attempt on human blood, but only 10-20% of them. But some specimens can become carriers of several infections at once, the most common of which is tick-borne encephalitis.
Symptoms of other infectious diseases
Any bite from an infected tick can result in a serious human disease. The situation is complicated by the fact that many diseases begin to manifest only a few days after the attack of the parasite. In addition to an increase in temperature, which is easily mistaken for signs of an incipient cold, there may be other consequences that will help determine that a person has been infected by a tick bite:
- blood pressure jumps, tachycardia (heart palpitations);
- tongue, runny nose, sore throat;
- nausea and vomiting;
- swollen lymph nodes and rash on the face are signs of typhus;
- bleeding from the nose, diarrhea and abdominal pain - indicate infection with tularemia;
- excessive sweating, chills, pain in the lumbar region, loss of consciousness - signs of hemorrhagic fever.
Important!
It is impossible to recognize a tick and determine by eye whether it is contagious or not. To clarify the diagnosis, it should be referred to the nearest laboratory or sanitary epidemiological station to determine the presence of pathogenic pathogens. If the test is positive, then it is urgent to consult a doctor about treatment.
If any unpleasant symptoms appear and you feel unwell during tick bites or after them, you should contact a general practitioner or infectious diseases doctor at the clinic, and in case of a serious condition, call an ambulance.
What to do if bitten by a tick - instruction
After returning from a walk in the woods or cottages, it is imperative to examine yourself, family and friends so as not to miss the settled tick on the leg or other parts of the body. If found, it must be quickly pulled out.
The place of the tick bite is usually colored in pink-red shades, which depends on the individual reaction of the victim's body. In the center there is a small depression in which you can find a stuck tick on the human body. It is held very tightly, so it is impossible to extract it in the usual way, without tearing off the head or the proboscis.If any of its parts remain under the skin, the inflammatory process may begin in the damaged area and the bite heals for a long time.
To avoid complications, the parasite should be twisted out of the skin with the help of improvised tools:
- The easiest method is to remove the tick with tweezers: taking the upper part of the body closer to the skin, it should be taken out in a circular motion counterclockwise. After such manipulations, the parasite's body gradually comes out. If you pull sharply, then in the hands will be a tick without a head.
- Another effective remedy is a small piece of ordinary sewing thread, from which a loop is made, put on a “bloodsucker” and begin to rotate in any direction, gradually pulling it out.
After the removal procedure, it is necessary to look at the condition of the tick: if it is alive, then it is better to place it in a jar for transfer for examination. If this is not necessary, then it can be burned and drained into the sewer. Then be sure to thoroughly wash your hands and tools.
First aid for tick bites
To avoid infection of the wound from a tick bite, you should properly handle the bite site.
For this, the following actions will be helpful:
- Wash hands with soap.
- Treat the wound with a disinfectant: alcohol, hydrogen peroxide.
- It is not recommended to apply coloring agents (brilliant green or iodine) in order not to change the picture of the affected area.
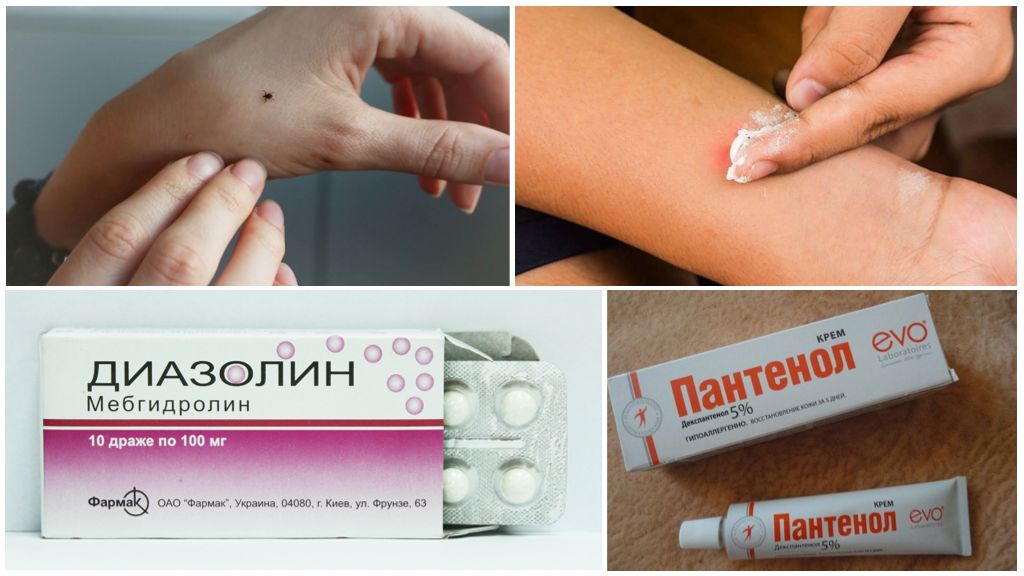
- If an allergic reaction is likely to occur, apply any soothing ointment: Fenistil-gel, Panthenol, Rescuer cream, etc.
- If there is a rash after a tick bite or other individual reaction, then an antihistamine should be taken: Diazolin, Tavegil, Loratadin, Erius, Cetrin, etc.
- To drink plenty of fluids, bed rest is recommended in the first days.
Tick bites in children
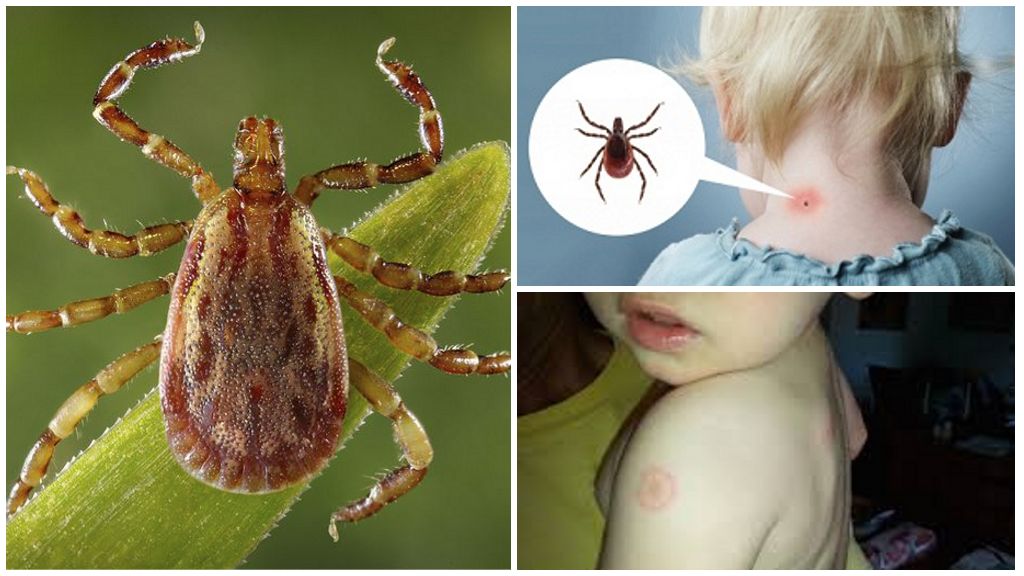
In babies, the reaction to a tick bite in a hand or other part of the body is manifested by a rounded redness or swelling. If the parasite is promptly and carefully removed, then after a few hours a small lump with a red rim swells up on the skin, which gradually begins to heal, as seen in the photo of a tick bite in children. Healing and reduction of swelling occurs within 2 weeks.
Important!
The children's body usually reacts more acutely to the saliva of parasites,therefore, when the first negative symptoms of a child appear in the form of dizziness, weakness, fever, photophobia within 3 hours after the bites, it is possible to draw a conclusion about a possible infection. Parents should consult a doctor, it is recommended to give immunoglobulin, anaferon or antibiotic Yodanthiprin.
What not to do with tick bites
When detecting signs of a tick bite or the parasite itself on its body, it is strictly forbidden to use the following actions:
- to lubricate the “bloodsucker” with vegetable oil, which, contrary to the prevailing erroneous opinion, not only does not force him to crawl out, but also stimulates him to regurgitate blood after suction, which increases the risk of infection and inflammation;
- cauterize the mite with caustic liquids (gasoline, kerosene) or a burning cigarette;
- sharply pulling it out, which always leads to a rupture of the calf, and the head remains under the skin, which, according to reviews about the tick bite, often leads to wound suppuration;
- try to crush the parasite;
- pick it out with a non-disinfected needle or other dirty objects.
All these actions increase the risk of infection of humans with bacteria and infectious diseases, lead to purulent processes in the epidermis.
Bite prevention
In order to avoid thinking about whether a tick bitten or not during a visit to a forest, a park or a dacha, and what consequences this may cause, you should take preventive measures that will protect children and adults from this problem:
- wear light-colored clothing, on which crawling insects are clearly visible, with long sleeves and adjacent cuffs;
- to process clothes with repellents or scaring acaricidal sprays, whose smells do not tolerate mites;
- beware of walking or sitting in the tall grass, where parasites lurk their victim in order to climb on it;
- before visiting the area where tick-borne encephalitis is common, it is recommended to make a prophylactic vaccine for the development of immunity;
- After the walk, carefully examine the clothes and skin for parasites that have stuck.
These recommendations will allow you to avoid the attack of "bloodsuckers" and the likely negative consequences.









 (votes: 5, Average rating: 4.60 out of 5)
(votes: 5, Average rating: 4.60 out of 5)