Varieties of flies with photos and descriptions
Content
- Housefly
- Hematophagous flies
- Flies necrophages
- Fly-smilnitsa
Flies appeared on the planet more than 250 million years ago. During this time, the paleomukhs managed to develop into more than 400 thousand species and adapt to any conditions of existence. This dipterous insect today cannot be found only beyond the Arctic Circle and in Antarctica. Flies took all possible for living organisms food niches. Some feed on the nectar of flowers, others on blood, others on decaying organic matter, fourth and fresh.Some earlier steppe and forest species of flies quickly "figured out" what benefits they would develop civilization and moved closer to human housing. It is necessary to move a couple of kilometers from the last dwelling, and these synanthropic flies cease to annoy. They are replaced by the remaining "wild" species.
Fly classification
Flies can not systematize so far, offering various ways of separating these insects into orders, genera, families, and so on. But the simple inhabitants of the planet are not very interested in such methods of classification as the shape of the seam, according to which the pupa bursts, or the length of the whiskers in a fly. But the food cravings of flies excite everyone, since the comfort of human existence depends on it. And the division of dipterans according to the food factor is quite clear and does not cause confusion.
According to the nature of nutrition of adults, flies are:
- nectarophagus;
- afagi;
- hematophagous;
- coprophages;
- necrophages;
- polyphages.
The second part of these words comes from the Greek phagos - “devouring” and indicates the type of food that each group eats.
The food of nectarophages is the nectar of flowers, the afagi do not eat at all, the hematophagous drink blood, coprophagous eat feces,necrophages are dead flesh, and polyphages have a very extensive food base. A vivid example of a polyphage is a housefly.
On a note!
Among coprophages and hematophages, there are two types of flies: obligate and optional. At the first larvae and imago feed on the same food. The second variety of food bases of larvae and imago are different.
Coprophagous
Obligate among others are some species of the family of real flies that live on pastures. These insects contribute to the decay of excrement in nature and it is difficult to attribute them to pests or dangerous flies. But sometimes they fly into homes, spreading the eggs of worms. In addition, these types of flies often settle in areas where animals are kept.
The facultatives are much more dangerous, since adult flies feed on excrement, but they also readily eat human food. Often these species arrive for food directly from the manure heap. Larvae food - excrement.
On a note!
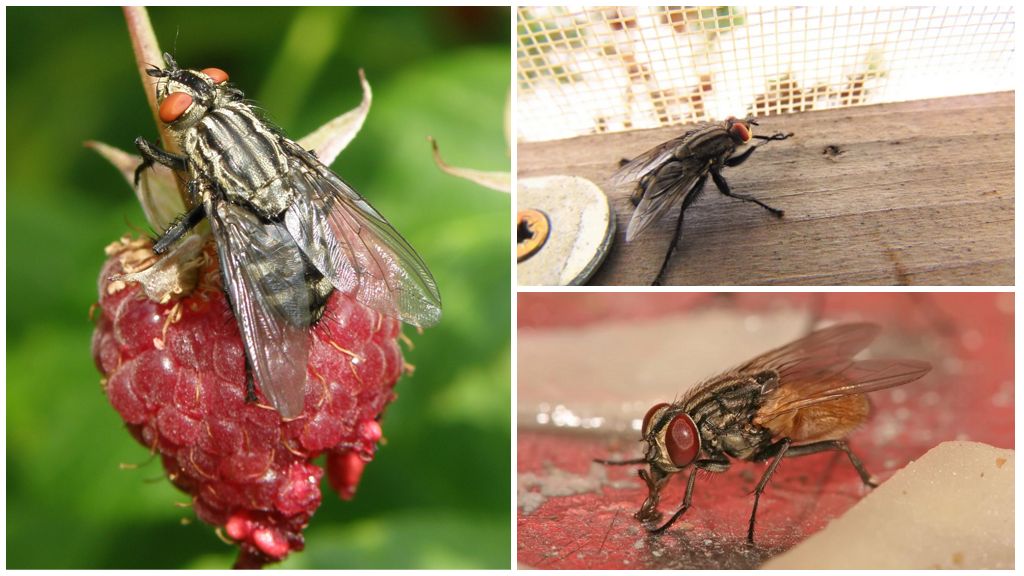
The most typical and common representative of elective coprophages - house (fly) fly. It is one of the most common types of flies in Russia, so adapted to life in human homes that it almost never occurs in nature.
Appearance of a housefly
In the photo of a house-fly when macro-magnification, you can clearly see all the details of the coloring. But when viewed with the naked eye, the fly looks gray.
This is a small insect with an average length of 7 mm. The color of the house flies is gray with four longitudinal black stripes on the chest. The belly is yellowish underside. The eyes are large, dark red. Eye device faceted. The male differs from the female by the distance between the eyes: in females, the length of the organ of vision is equal to the distance between them; male eyes are spaced 2/3 of the length.
Nutrition
A housefly is an insect that cannot bite through human skin, although the female needs protein food to breed. This species of flies eats only liquid food. When finding solid pieces of organic matter, a housefly dissolves them in saliva before use.
In this way she can "bite" a person. Trying to dissolve the skin with saliva, the fly causes a sharp pain. Similar sensations would have caused an acid burn. But the marks on the body of such "Bite" does not remain.
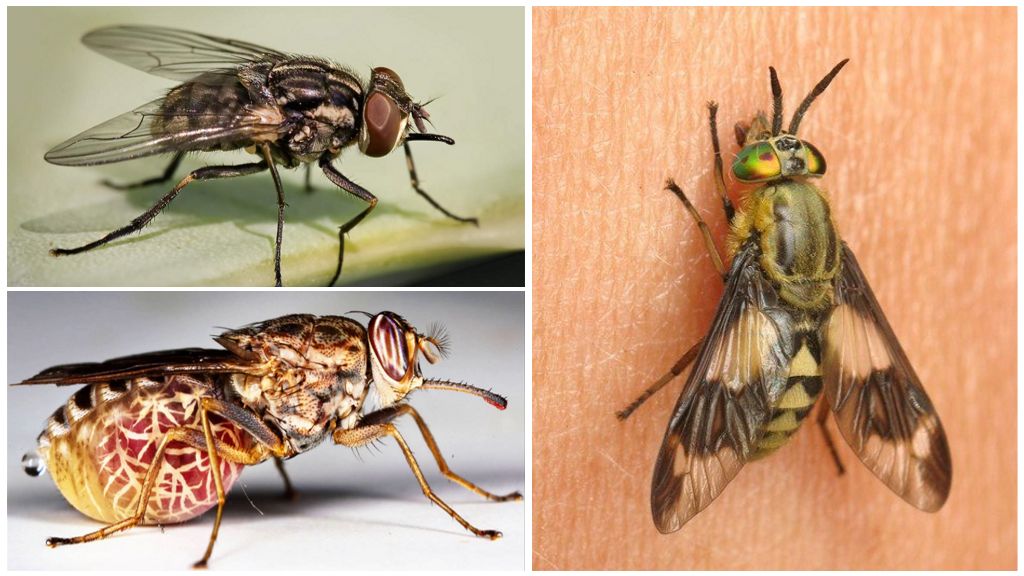
Hematophagous
Flies that bite are obligate hematophagous. This species feeds on blood in the imago stage. Larvae develop in decaying organics.Obligatory hematophagous include: gadfly, autumn fire and tse-tse, often called flies killer.
Interesting!
The biggest flies are called horseflies because of their thirst for blood. The female, trying to get drunk with blood and lay eggs, feels no danger, does not notice anything around and often dies from the tail of an animal or a human hand.
In gadflies, females differ from males in that they usually do not even see the latter. Horsefly males feed on nectar and are not attacked by mammals.
Some kinds of gadfles have green eyes because of what they are often confused with others. large flies with green eyes - gadfly-afagami.
All obligate hematophagous have an oral apparatus adapted to the extraction of blood.
Facultative hematophages are not able to independently extract blood from the victim's body. They feed on secretions of the skin and mucous membranes. Willingly drink blood, protruding from fresh wounds. In addition to secretions, they feed on mammals excrements and vegetable juices. Larvae develop in feces.
A typical representative of the optional hematophagous is a market fly, very similar to a room fly, but living only in the southern regions.Distributed throughout Central Asia and the Caucasus. In Russia lives in a subtropical zone.
Necrophages
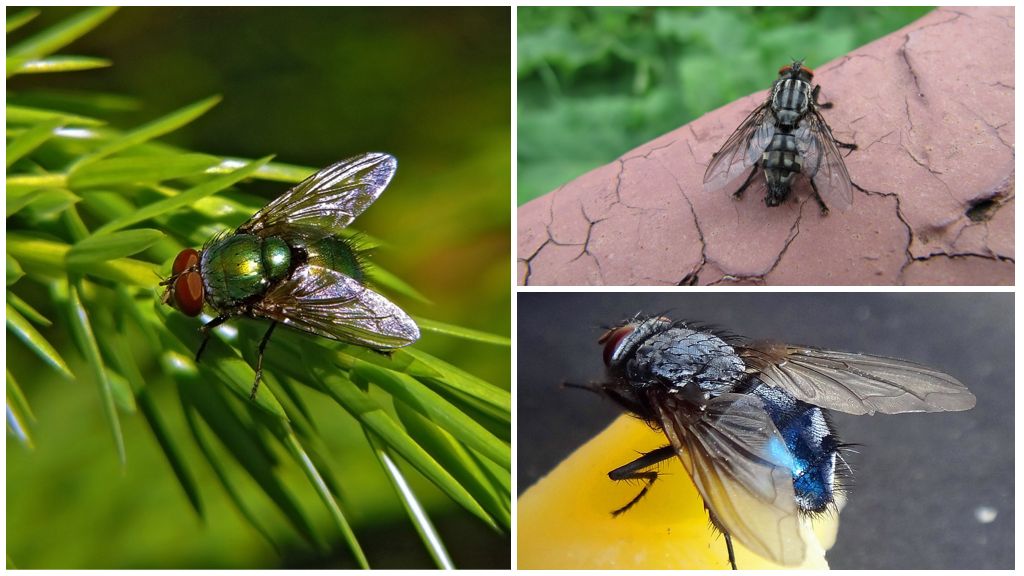
The names of species of flies can often be misleading. Such a species as “trash fly” does not exist in nature. Under this name most often hides lucily, belonging to the group of necrophages. On the same garbage can be found any synanthropic species, including fruit flies. The group of necrophages of the most famous flies includes:
- lucily (green);
- gray meat;
- blue meat.
All of them feed on animal carcasses, but also include food waste, vegetable juices and excrement in their diets.
Interesting!
Necrophages are easy to distinguish from other dipterous: all these flies with red eyes. Some eyes may have blood red (gray meat fly) or brick (green).
Lucily
Very common and well known emerald green fly able to lay eggs on meat left unattended for a couple of minutes.
Often they lay eggs in open wounds, where the larvae begin to develop, eating rotting flesh. The main habitat of these dipterans near human habitation is slaughterhouse.But also larvae can develop in animal excrement. The development of the larvae from the egg takes 1-2 days.
Blue meat
Insect is medium in size. Distributed over all continents. As well as green prefers slaughterhouses and decaying meat.
Gray meat
One of the most dangerous carrion flies. It looks like a regular room, but larger and with clearly visible bright red eyes on the head. Type of viviparous. The female only needs to touch the belly of the meat in order to lay the larva. When the larva goes outside, it immediately begins to bite into the meat. The place of introduction of the larvae can be determined by the appearance of liquid from decaying meat.
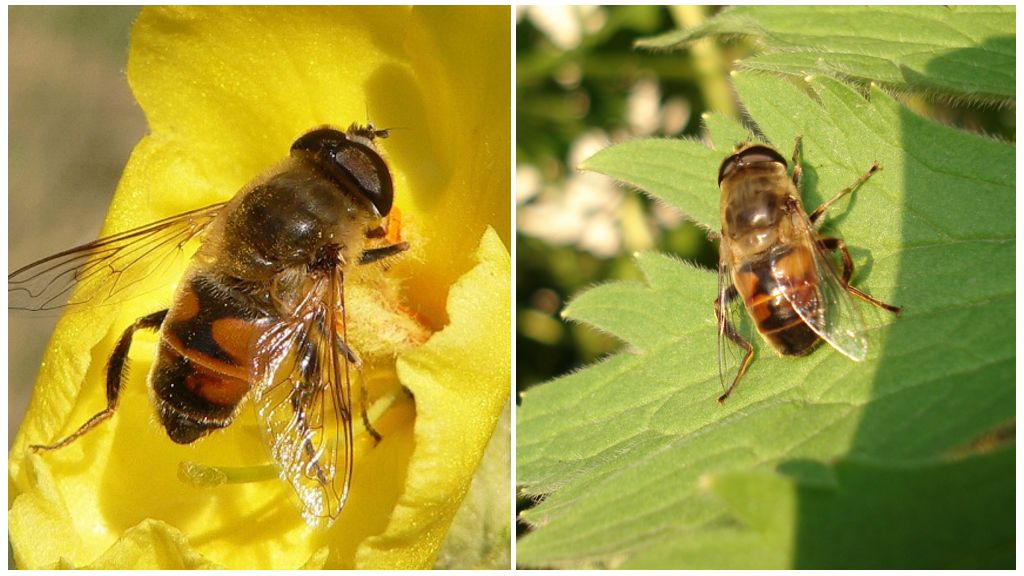
Nectarophage
This group includes a fly-ylitsa - an insect similar to a bee, but with two yellow specks on the upper side of the abdomen. Sometimes these specks have a reddish tint.
A beehive can be harmful to a person only if its eggs fall into the gastrointestinal tract. Considering that the larvae of the larvae develop in the pits with sewage, the probability of the eggs of the eggmaker entering fresh food is very small.
Afagi
Species that do not consume any food in adulthood.Particularly dangerous afagov include gadfly, the larvae of which feed on the soft muscle tissues of the host or parasitize in the intestine.
On a note!
Contrary to common belief gadfly does not bite or lay eggs under the skin.
Eggs of gadfly, depending on the species, either stick to the animal's fur, or lay on the grass, or injected into the nose and eyes. The hatched larva itself makes its way under the skin or into the intestines.
Piedrokrylki
This family of flies with spotted wings. Most of them are small, only a few mm in length. Some species can reach 2 cm. For humans, they are harmless, but cause serious damage to crops.
Among the pied fleet is an exotic for Russian Mediterranean fruit fly with a red belly. Due to its size (up to 5 mm) and its color similar in color, the details of which are difficult to distinguish without a microscope, this fly can be easily confused with fruit fly.
The Mediterranean fly is not included in the number of Russian pests, but can be delivered along with citrus fruits - the main food for its larvae.