How can I get Giardia
Content
- Giardiasis
- Waterway transmission lamblia
- Contact-household transmission lamblia
Giardiasis is a common disease among people of different ages. The main source of infection is an infected person. Single-cell microorganisms multiply rapidly, for a long time they exist in the environment.Epidemiologists identify several basic ways of how Giardia is transmitted from person to person.
Invasive (infectious) parasite forms
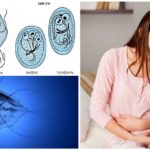
Being the simplest microorganisms, Giardia exists in two life forms - active and inactive. Living parasites are viable in an anaerobic environment, quickly die outside the human body. Inactive spore form lamblia - cysts, covered with a dense shell. They serve as the primary means of transmitting giardiasis from person to person.
Trophozoites
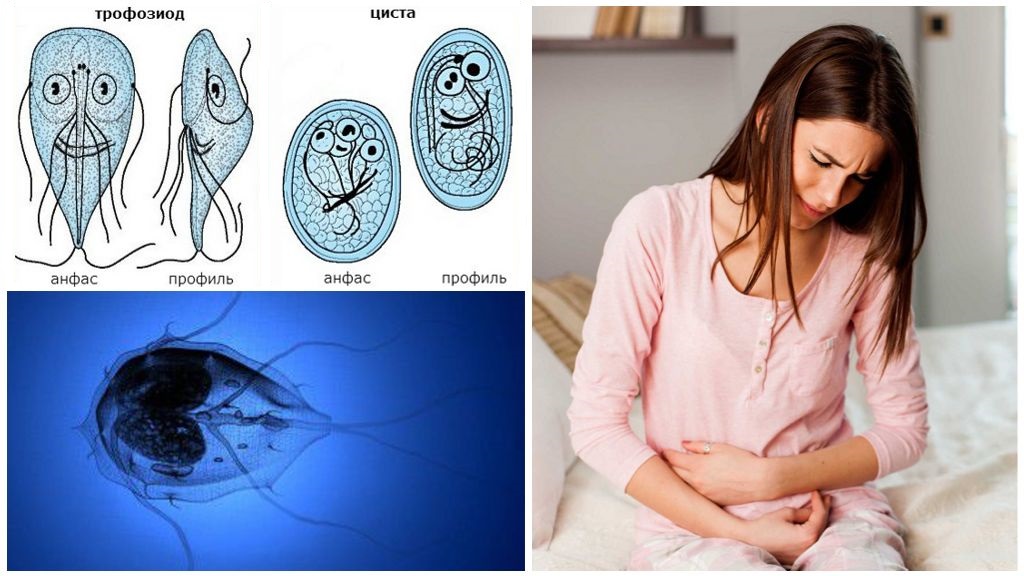
Living parasites (trophozoites) are very active, feed on solutes and multiply many times by simple division. They have a unicellular structure with two nuclei and a large suction cup. Giardia are moved with the help of two pairs of motile flagella. Trophozoites live in the small intestine, able to move to other internal organs. In the large intestine, they become coated, turning into cysts.
On a note!
Live trophozoites enter the environment with liquid faeces during diarrhea. Giamblia are contagious at room temperature for 30-60 minutes. In the aerobic environment, they soon die without representing an invasive hazard.Infection with giardiasis is possible when a healthy person comes in contact with fresh fecal masses of an infected host host.
Cysts
Mostly infected with Giardia when swallowing cysts, which are characterized by increased viability. They retain the invasive properties under conditions of temperature differences (up to -13 ° C frost and up to + 70 ° C heat), aggressive media (detergents, bleach). Cysts at room temperature are contagious for 3-4 weeks, in warm waters - up to 6 months. They die under the influence of disinfectant solutions, high temperatures (above + 70 ° C), in arid climate.
On a note!
Cysts enter the environment with feces, spread by air and water over long distances. For a long time they are in a state of anabiosis on plants, furniture and household items, animal hair. With the faeces of an adult infected with giardiasis, up to 12 million cysts are excreted.
The main ways of transmission of giardiasis
Favorable conditions are necessary for the development of Giardia - an anaerobic, warm and humid environment. These requirements are met by the human body, which is the sole owner of the parasite. The invasive properties of cysts appear only after they are swallowed.Only in the cavity of the small intestine, mobile trophozoites exit through the dissolved membrane. The main ways of infection Giardia:
- oral-fecal;
- water and alimentary;
- contact-household and direct.
Giardiasis most often affects children of the younger age group attending preschool institutions. Among them, almost all methods of lamblia invasion are common. Less commonly, the disease is found in adults who neglect personal hygiene and sanitation.
Oral-fecal infection
This option is common in home farms and residential areas where there is no centralized sewage system. Cesspools become a source of contamination of groundwater and surface water, garden plots, adjacent territories. Lack of personal hygiene contributes to the massive infection with cysts Giardia and Giardiasis among the local population.
On a note!
In children, the most common oral-fecal route of infection. They forget to wash their hands after being in the toilet, they collectively use personal hygiene items. If Giardia is found in a child in a preschool institution, in a short time the infection spreads to the whole group of children.
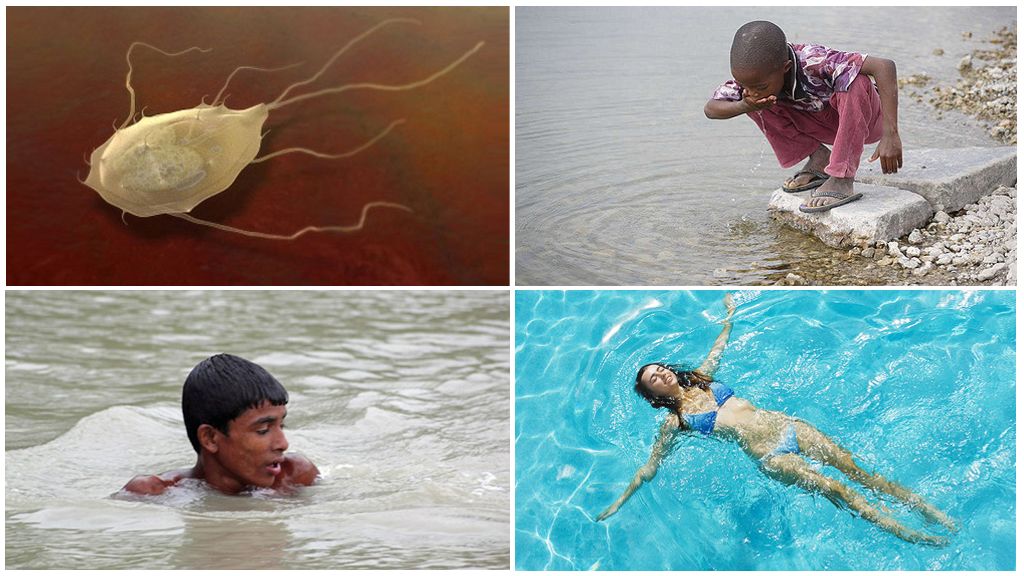
Waterway
In aquatic environments Giardia are contagious for a long period of time - up to 6 months or more. Here cysts are in a state of anabiosis, pose an increased threat to humans.
The risk of infection with giardiasis increases in the following cases:
- involuntary swallowing of river or lake water while bathing;
- use of water from open reservoirs for drinking purposes;
- accidental release of sewage into the water supply system;
- the use of raw contaminated water from a water supply system;
- the use of water from wells located near cesspools;
- swimming in pools with insufficient cleaning system.
In almost all open reservoirs, there are Giardia cysts, ready at any moment to invasion. Parasite spores are often found in weakly chlorinated water. For the development of giardiasis in a child enough to swallow ten cysts. Of these, twice as many active trophozoites form in the small intestine of an infected person.
On a note!
Lamblia cysts die with increased salt content. For this reason, they are not found in seawater. Giardia through saliva are not transmitted, because its alkaline environment for them is destructive.
Alimentary infection
Transmission of Giardia through dirty hands and products is one of the most common causes of giardiasis. The use of dirty fruit and vegetable products, poor-quality heat treatment, the abundance of flies significantly increases the risk of parasite infestation.
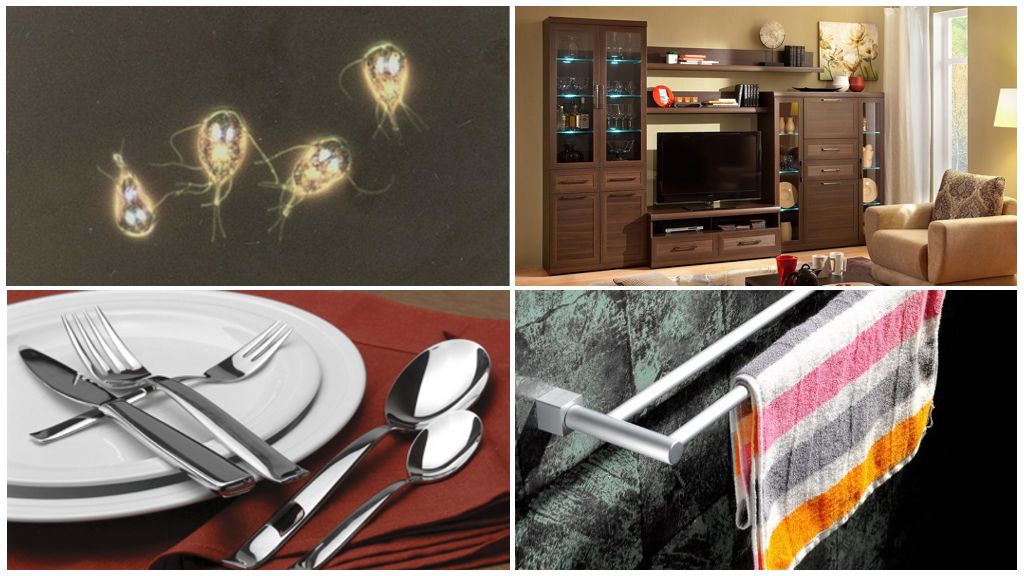
Contact-household way
Direct contact with household items is one of the probable ways for Giardia infection in adults and children. Any things touched by an infected person pose a potential threat to healthy people:
- furniture, computer keyboard, books;
- personal hygiene items - towels, washcloths;
- dishes, cutlery, pens, cosmetics.
Cysts and sometimes trophozoites are transmitted from child to child through common toys, clothing, and bedding.
On a note!
Giardiasis is a rapidly spreading parasitic disease. The detection of lamblia in one family member is indirect evidence of infection of all households.
Pets
On the question of whether animals are infectious with respect to human lamblia, epidemiologists unanimously give a negative answer.In their body live other parasites that do not pose a threat to humans. However, pets can be carriers of human Giardia cysts. Spores get on wool during a street walk, swimming in water, contact with infected people. When stroking an animal, cysts pass to the fingers and are swallowed by a human in violation of personal hygiene.
Other modes of transmission
Usually Giardia is not transmitted through a kiss, but this route of infection is possible in conjunction with oral-fecal infection. Failure to follow basic rules of personal hygiene provokes the development of giardiasis. Direct infection with Giardia sexually occurs. However, this option is possible in violation of the standards of sanitation and hygiene. To include methods of infection - the exchange of handshake, the habit of biting nails, wearing common wardrobe items.