Moose lice
Content
- Moose lice
- Animal pest
- Louse bites
People who love tourist trips or hiking in the woods for mushrooms, do not interfere with knowing that there they can expect not only pleasant impressions, but also insects-bloodsuckers. The best known pests are: mosquitoes and pincers, but there are some unfamiliar to a wide range of tourists, for example, elk louse.
Description of elk lice
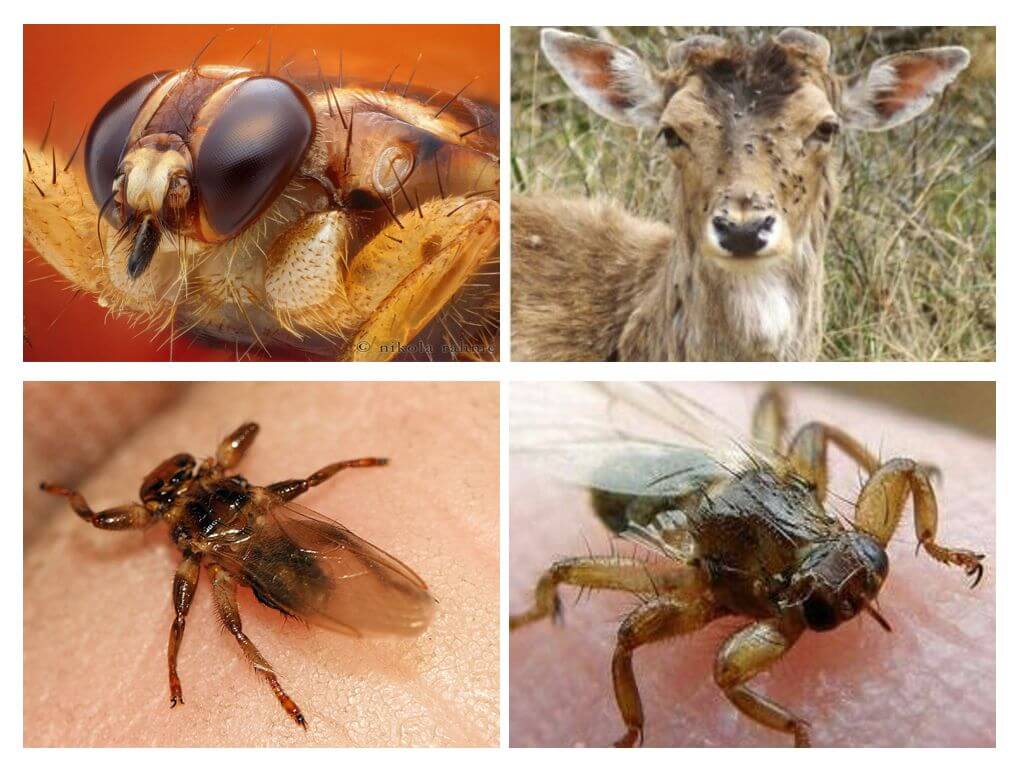
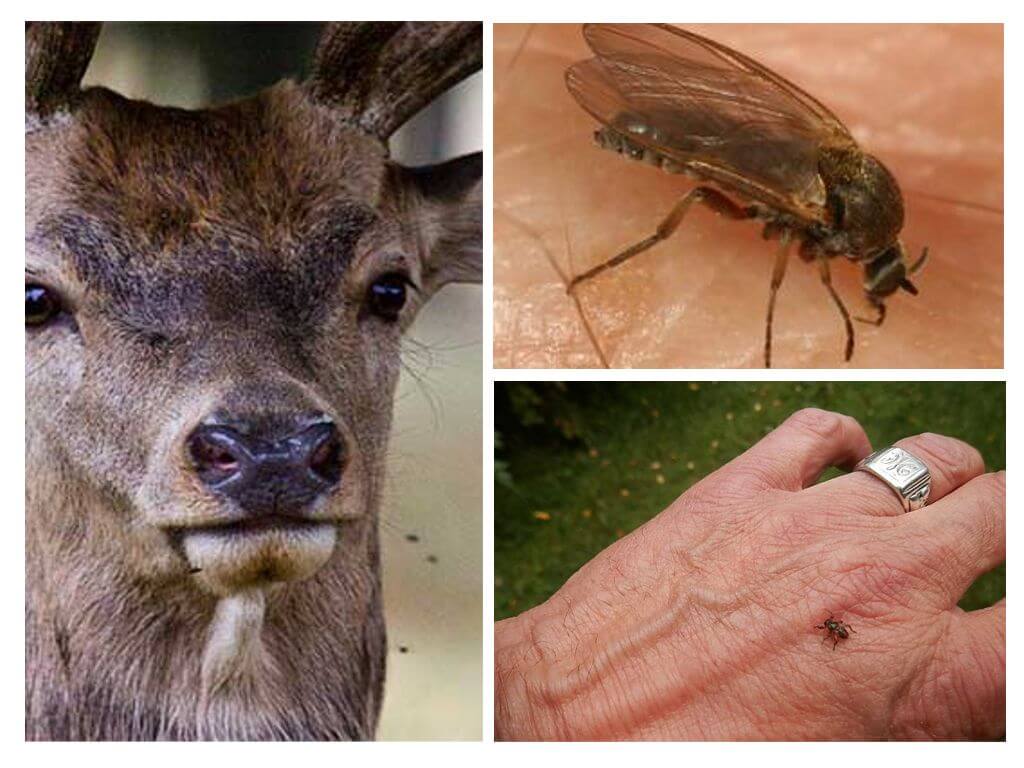
This insect has many more names: deer fly, elk mite, etc., which it received because of the names of animals-breadwinners: elk, deer, deer. They can also settle in the fur of smaller animals (bears, foxes, wild boars, etc.).
On a note!
Moose lice belong to the bloodsucker family and are very similar to normal a flea and ticks, which is why they are often confused with them.
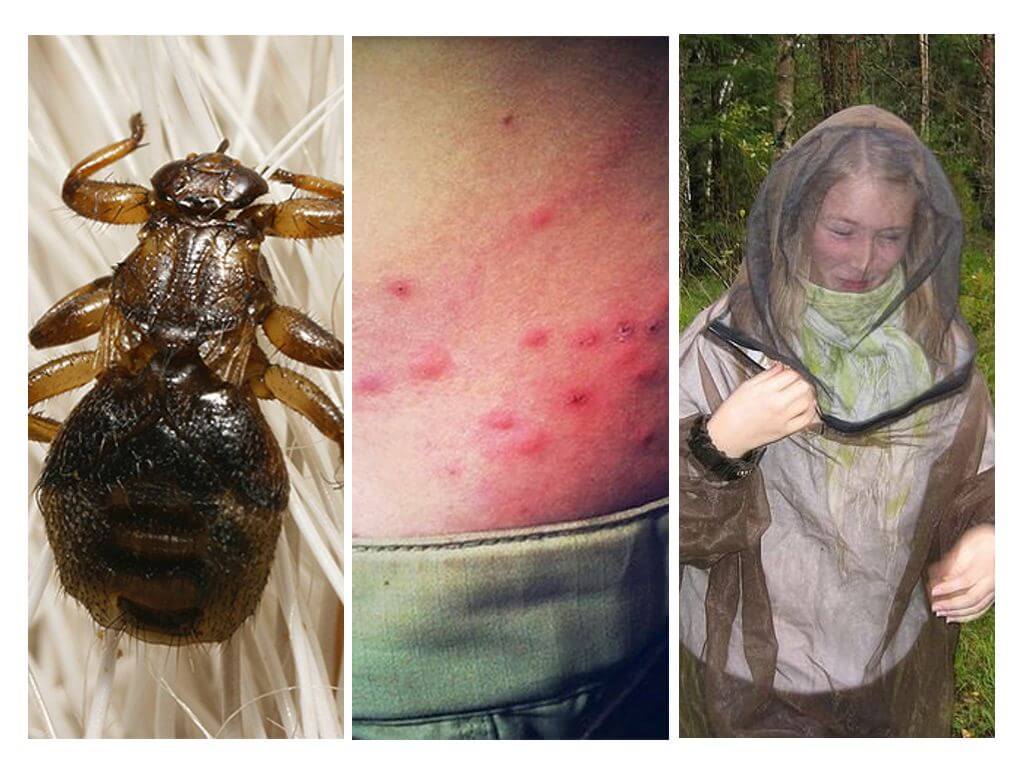
The body is light brown in size 2-5 mm with three pairs of paws with claws, with which they cling to the animal hair (see photo of elk lice). These insects have wings, although they rarely use the proboscis, through which they suck blood. Wings 5-6 mm long, they use only when searching for a new owner, and then shed them and burrow into the animal's fur.
On the head, such a louse has 2 large eyes, occupying almost a quarter of its volume, but in addition - 3 more ordinary eyes (you can see this in the photo).
Distributed over a large territory of the European part of Russia, Siberia, in northern China, in the Scandinavian and North American countries. On one animal 200-1000 such parasites can settle.
Life cycle
Moose lice live in pairs, the fertilized female carries an egg in which the pupa develops after a certain time, and then the larva. After 16–18 days, it gives birth to a 3-4 mm larva, called the prepupa, which after 2 hours turns into puparia.The birth of the next pupa occurs in a couple of days, in the course of her life the female has time to give birth to 20-30 larvae.
Pupariums with a hard shell fall to the surface of the earth in the autumn-winter time (from October to March), where they are within six months of their development until August. After that, the larvae hatch young flies with wings (see elk lice in the photo), which are actively looking for their owner and breadwinner, flying on the grass and bushes. After its discovery flies settle in the wool, dropping wings.
Thus, the entire life cycle of moose lice lives for 5-6 months, dying in the spring after the active laying of pupae.
During its short life, the insect usually lives on one animal, under adverse circumstances (death of the host), migrates to another. Every day the parasite feeds up to 18 times the blood of its breadwinner, sucking 1 mg per session. Due to the fact that there can be a lot of such lice on an animal, severe blood loss leads to its exhaustion and death.
On a note!
Most often, the pests settle on forest animals, but are also found among livestock (goats, cows, sheep, etc.).
Danger from elk lice attacks
Moose louse is dangerous only for its breadwinners - forest animals. For humans, it is less dangerous. Cases of such insect bites are found in foresters, hunters and mushroom pickers.
Elk lice bite is quite painful and is accompanied by inflammation and compaction, there is also a strong itch that can lead to scratches and scratching. The elk flies themselves do not spread the infection, but through wounds in the bitten places a person may well carry the infection. There is also a risk for people prone to allergies.
Interesting!
If such a fly clings to the skin of a person, then it is not easy to remove it because it clings tightly to the skin with its claws.
Precautions and protection against elk lice
The most reliable way to protect against elk flies is to wear protective clothing in the forest: overalls or jackets with pants, which should have cuffs tight to the body, the pants should be tucked into socks and boots. It is also better to protect the head with a mosquito net or head covering. Specialized protective clothing models.
When hiking in the forest to scare away insects use mosquito repellents or tick remedies in the form of sprays that are applied to the skin and clothing. Such drugs have a wide spectrum of action and affect many blood-sucking insects.
If the insect has adhered to the skin, then it can be removed in the following ways:
- using a durable thread, a loop is made, which is tightened onto the louse body, then twisting and swinging the thread, the insect can be pulled out;
- you can remove the parasite with tweezers, only with care so as not to tear off its upper part, since the bottom will then remain under the skin;
- using sunflower oil, which louse is smeared and waited for when she comes out (15-20 minutes).
After the insect is removed, the wound should be treated with an antiseptic: hydrogen peroxide, etc. The bitten itchy place should not be combed so as not to cause an infection, but rather use folk methods: apply ice, tinctures of aloe and calendula, which will also relieve inflammation. If an allergic reaction is necessary to take an antihistamine.
If, after visiting the forest, elk lice were found on the body or clothes, then it is necessary to tidy up everything in hot water, bathe and wash your hair thoroughly.For better protection and destruction of pests, insecticidal preparations can be used, which are used to pediculosis treatment.