What is dangerous pediculosis
Content
- Lice Discomfort
- Danger of pediculosis
- Lice disease
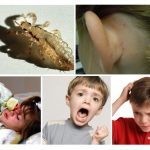
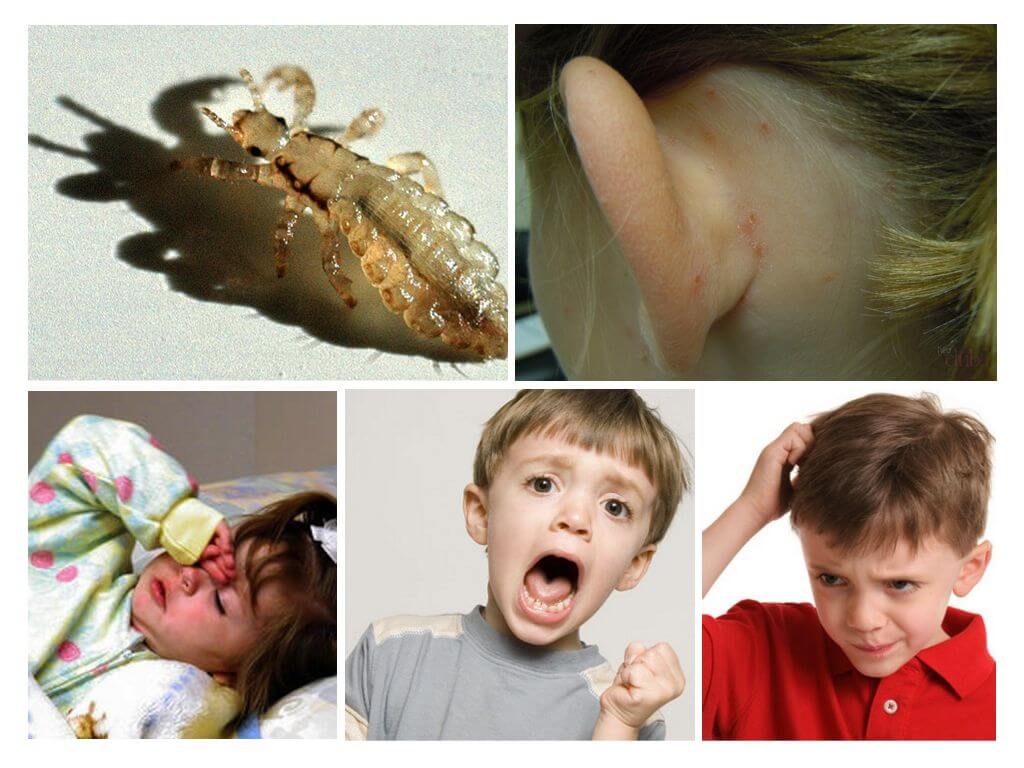
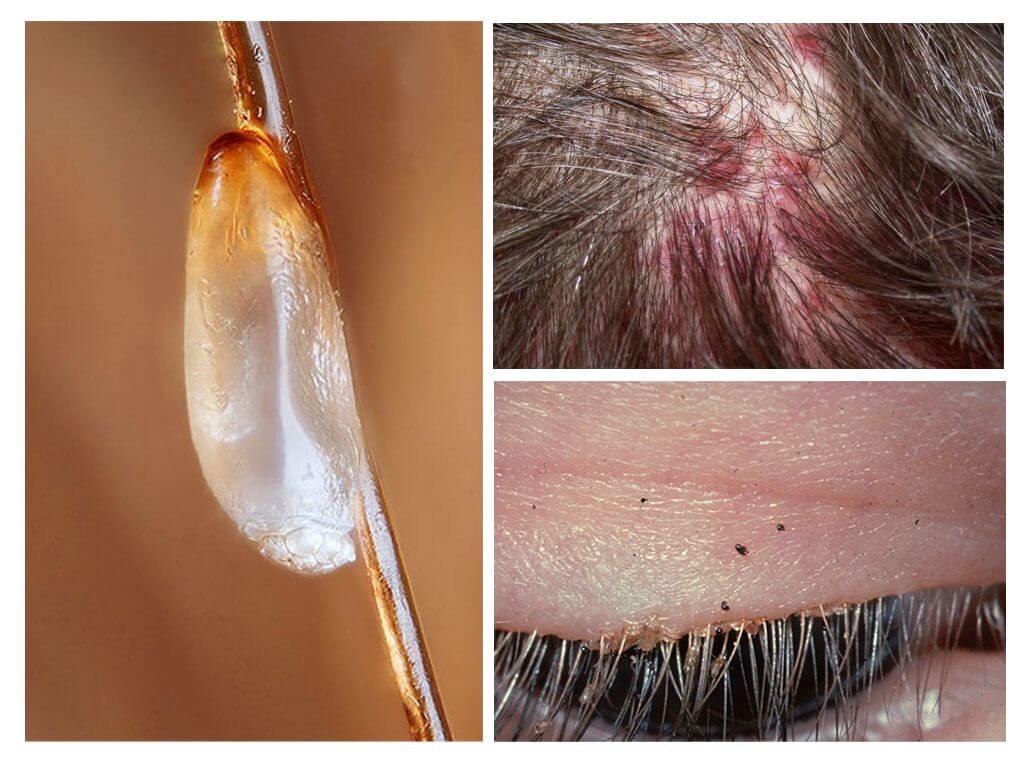
Head lice perceived as harmless and unpleasant bugs, which are dangerous only because they cause itching in places of bites. But blood-sucking parasites are able to endure serious infectious diseases, provoke an allergic reaction, and cause the skin to coarsen. It is worth figuring out how dangerous lice on the head is for humans and whether it is worthwhile to fear insects that parasitize other parts of the body.
Danger to the child
Children more than adults suffer from pediculosis. Their fragile bodies are susceptible to illness and are more likely to be allergic to irritants.
Interesting!
Even a newborn baby can get pediculosis. Considering how lice are transmitted, parasites can transmit to him mom or older sisters and brothers.
What is dangerous pediculosis in children:
- disrupts sleep;
- leads to impaired concentration;
- makes the child restless;
- provokes the appearance of purulent wounds.
The disease prevents children from concentrating on their studies. They become capricious, often crying and complaining of dizziness and severe itching. Discomfort can persist up to three days after insect hatching.
Pediculosis in sensitive and vulnerable children can lead to fears:
- insect phobia - entomophobia;
- fear of parasites - parasitophobia.
A small person may feel that someone is crawling over his skin, and any insect will start causing a panic attack.
Children up to three years old with lice can react with fever, nausea, and swollen lymph nodes. The waste products of insects provoke the appearance of allergies.
Danger for adult
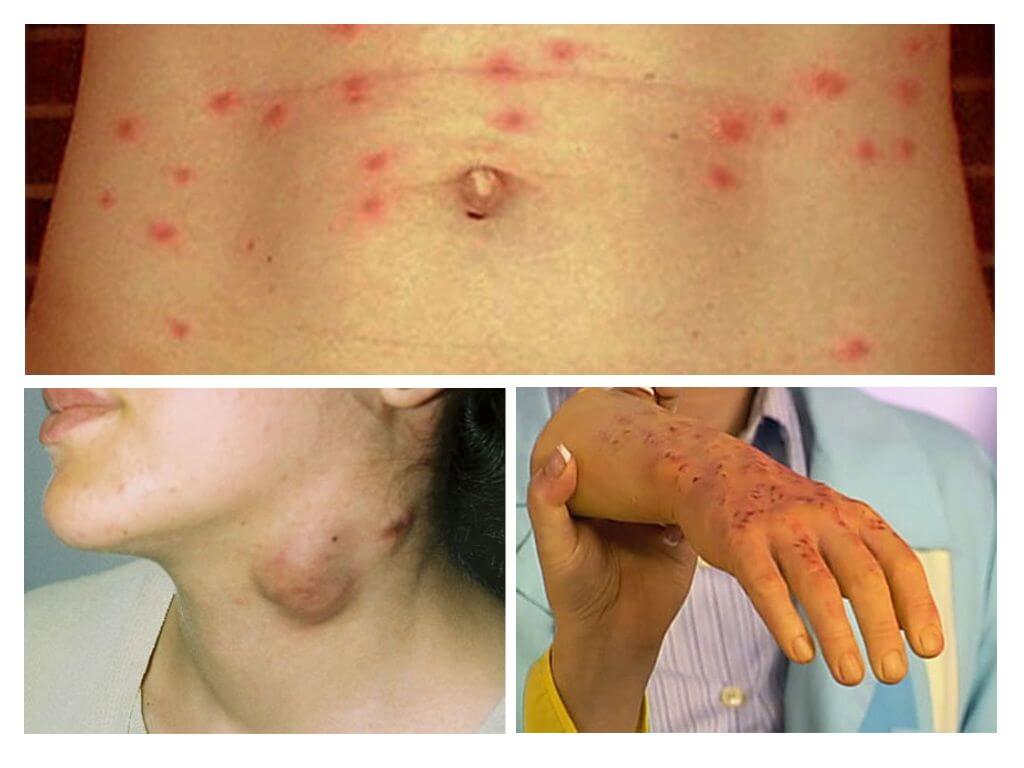
Adults are less likely to experience lice, but this does not mean that head lice goes completely without a trace. Insect causes severe itching on the head and leads to scratching. The wounds themselves are not dangerous, but through them infection easily gets into the human body.
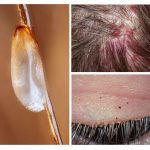
Insect nit is also not particularly dangerous. She only spoils the hair on her head and confuses them. Sometimes you have to completely cut the hair to get rid of lice and nits.
What is dangerous pediculosis for an adult:
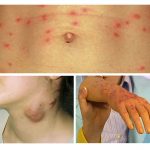
- Coarsening of the dermis. Louse injects a special substance into the wound that prevents blood from clotting. Louse bites in the same place cause the appearance of melanosis. Skin color changes, and the derma itself becomes coarse and begins to peel off. With constant scratching, pus is released from the wound, which entangles the hair on the head and forms a crust, under which the wound is soaked.
- Allergy. Excretions of parasites that fall into open wounds cause purulent inflammation of the skin, folliculosis, dermatitis, eczema. A person suffers from severe itching of the head. Without treatment, the patient’s condition is getting worse.
- Conjunctivitis. Living on the head of a man lice this disease can not cause. Eye inflammation occurs due to pubic licewhich settles on the eyebrows and eyes.
Infection with head lice prevents a person from leading an active life and communicating with other people. Pediculosis is easily transmitted, so the patient has to become a recluse until recovery.
On a note!
The louse settles even on the washed head, and pediculosis can be picked up in public transport, a bath, a pool.
Cootie at night is the cause of unbearable itching. A person can not sleep, suffering from painful parasite bites. Head louse appearance causes severe discomfort after washing hair.
Chronic Pediculosis
The disease can become chronic and poison human life for a long time. Under chronic pediculosis, the skin becomes coarse, acquires a brown tint and begins to peel off. Insect bites on the head merge into one spot that extends beyond the hairline.
On a note!
Often with chronic lice on the body, several types of parasites parasitize at once.
The human body adapts to this type of head lice.Permanent itching ceases to bother, but the risk of contracting a fatal disease increases significantly. In addition, lice get used to poisonous antiparasitic agents and getting them out is getting harder.
Lice on the head are also dangerous due to the fact that they can in a few generations create a population of parasites living in clothes.
What diseases carry lice
Blood-sucking parasites cause serious diseases. It is difficult to pick up a fever or typhoid from an insect, but no one can guarantee that this disease will not affect you.
Typhus
The disease is provoked by rickettsia. Carriers can be a louse living on the head and clothing. The bacterium enters the human body through an open wound along with insect feces.
Typhus fever is manifested by the following symptoms:
- heat;
- damage to the nervous system;
- fever;
- violation of the heart and blood vessels;
- rash.
In civilized countries, outbreaks of disease do not occur. But rickettsia can live for a long time in the human body. With the deterioration of living conditions, it manifests itself. Prevention of pediculosis reduces the risk of developing typhus.
Relapsing fever
The disease causes borrelia. The bacterium enters the open wound after the bite of a blood-sucking insect. Pest living on the head, the disease can not tolerate. A person becomes infected because of a louse.
On a note!
There is a vaccine against typhus that protects the human body for several years. It is recommended to do to those who are going to go to India or Africa.
The symptoms of relapsing fever are as follows:
- fever;
- headache;
- severe joint pain;
- vomiting and nausea.
Borrelia secretes endotoxin, which damages the liver, nervous and circulatory systems. Bacterial antibodies cause microinfarction.
Quintan
Volyn fever carries clothes louse. The disease does not end with the death of a person, but this does not mean that it is not dangerous.
Symptoms of the disease are as follows:
- fever, which then subsides, then returns;
- chills;
- joint pain;
- Pain in the eyes.
Volyn fever lasts six weeks, and then passes.
Tularemia
Carriers of the disease are animals, but blood-sucking parasites can spread tularemia among people.
Symptoms of the disease look like this:
- chills;
- confusion;
- heat;
- pain in the limbs;
- headache;
- dizziness.
Pediculosis adversely affects a person’s life. Therefore, when an insect is found on the head, you should consult a doctor who will prescribe an antiparasitic drug. Do not forget about prevention. Avoid contact with people at risk, use only your own comb, change bed and underwear in a timely manner, wash your head twice a week.